Data cleaning¶
This section describes the data cleaning process for FinTrack. It covers how raw bank data is standardized, cleaned, and imported into the database.
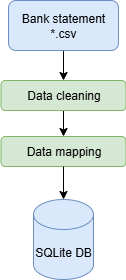
workflow data cleaning¶
Submodules¶
db_update.py module¶
db_update.py¶
This module provides tools for importing, cleaning, and unifying bank transaction data from various CSV formats into a single SQLite database. It supports multiple banks, automatic column mapping, duplicate detection, and robust logging.
Main features: - Automatically detects and maps columns from different banks to a unified schema. - Handles various encodings and CSV header formats. - Cleans and normalizes data for consistency. - Generates a unique hash for each transaction to prevent duplicates. - Saves all transactions into an SQLite database. - Logs all processing steps and errors for traceability.
- Usage:
Run this script to process all CSV files in the 02_raw_data directory and update the bank_statements.db database.
- 03_data_cleaning.db_update.create_transactions_table(db_path, table_name='transactions')¶
Create the transactions table with all possible columns and a unique constraint on transaction_hash.
- Parameters:
db_path (str) – Path to the SQLite database file.
table_name (str, optional) – Name of the table to create (default is “transactions”).
- Returns:
None
- 03_data_cleaning.db_update.detect_bank_name(filename)¶
Extract only the bank name from filename (without extension and year/suffix).
Examples
‘Bank_A-2024.csv’ -> ‘Bank_A’ ‘Bank_B_2023.csv’ -> ‘Bank_B’
- Parameters:
filename (str) – The filename to extract the bank name from.
- Returns:
The extracted bank name.
- Return type:
str
- 03_data_cleaning.db_update.find_header_row(file_path, sep=';', encoding='utf-8')¶
Find the header row in a CSV file by matching known column names.
- Parameters:
file_path (str) – Path to the CSV file.
sep (str, optional) – CSV separator (default is ‘;’).
encoding (str, optional) – File encoding (default is ‘utf-8’).
- Returns:
The row index of the header.
- Return type:
int
- Raises:
ValueError – If the header row cannot be found.
- 03_data_cleaning.db_update.load_csv_with_mapping(file_path, bank_name, sep=';')¶
Load a CSV file, map its columns to unified names, clean and convert data types, and return a DataFrame ready for database insertion.
Tries UTF-8 encoding first, then falls back to ISO-8859-1.
- Parameters:
file_path (str) – Path to the CSV file.
bank_name (str) – Name of the bank (used for the ‘bank_name’ column).
sep (str, optional) – CSV separator (default is ‘;’).
- Returns:
DataFrame with unified columns and a transaction_hash column.
- Return type:
pandas.DataFrame
- Raises:
ValueError – If the file cannot be read with the supported encodings.
- 03_data_cleaning.db_update.row_hash(row)¶
Generate a SHA-256 hash for a row based on all available data.
- Parameters:
row (pandas.Series) – A row of transaction data.
- Returns:
The SHA-256 hash of the row as a hexadecimal string.
- Return type:
str
- 03_data_cleaning.db_update.save_to_sqlite(df, db_path='C:\\public_projects\\portfolio\\FinTrack\\03_data_cleaning\\bank_statements.db', table_name='transactions')¶
Save the DataFrame into an SQLite database, ignoring duplicates.
Logs the number of records saved and duplicates skipped.
- Parameters:
df (pandas.DataFrame) – DataFrame to save.
db_path (str, optional) – Path to the SQLite database file.
table_name (str, optional) – Name of the table to save to.
- Returns:
None
- Raises:
Exception – If there is an error saving to the database.